- Oman
-
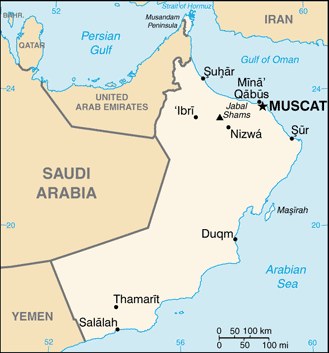 Introduction ::OmanBackground:The inhabitants of the area of Oman have long prospered on Indian Ocean trade. In the late 18th century, a newly established sultanate in Muscat signed the first in a series of friendship treaties with Britain. Over time, Oman's dependence on British political and military advisors increased, but it never became a British colony. In 1970, QABOOS bin Said Al-Said overthrew his father, and he has since ruled as sultan. His extensive modernization program has opened the country to the outside world while preserving the longstanding close ties with the UK. Oman's moderate, independent foreign policy has sought to maintain good relations with all Middle Eastern countries. Inspired by the popular uprisings that swept the Middle East and North Africa beginning in January 2011, Omanis began staging marches and demonstrations to demand economic benefits, an end to corruption, and greater political rights. In response to protester demands, QABOOS in 2011 pledged to implement economic and political reforms, such as granting legislative and regulatory powers to the Majlis al-Shura and introducing unemployment benefits. In August 2012, the Sultan announced a royal directive mandating the speedy implementation of a national job creation plan for thousands of public and private sector jobs. As part of the government's efforts to decentralize authority and allow greater citizen participation in local governance, Oman successfully conducted its first municipal council elections in December 2012. Announced by the Sultan in 2011, the municipal councils will have the power to advise the Royal Court on the needs of local districts across Oman's 11 governorates.Geography ::OmanLocation:Middle East, bordering the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, and Persian Gulf, between Yemen and UAEGeographic coordinates:21 00 N, 57 00 EArea:total: 309,500 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 71land: 309,500 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than KansasLand boundaries:total: 1,374 kmborder countries: Saudi Arabia 676 km, UAE 410 km, Yemen 288 kmCoastline:2,092 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmClimate:dry desert; hot, humid along coast; hot, dry interior; strong southwest summer monsoon (May to September) in far southTerrain:central desert plain, rugged mountains in north and southElevation extremes:lowest point: Arabian Sea 0 mhighest point: Jabal Shams 2,980 mNatural resources:petroleum, copper, asbestos, some marble, limestone, chromium, gypsum, natural gasLand use:arable land: 0.1%permanent crops: 0.12%other: 99.77% (2011)Irrigated land:588.5 sq km (2004)Total renewable water resources:1.4 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 1.32 cu km/yr (10%/1%/88%)per capita: 515.8 cu m/yr (2003)Natural hazards:summer winds often raise large sandstorms and dust storms in interior; periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:rising soil salinity; beach pollution from oil spills; limited natural freshwater resourcesEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:strategic location on Musandam Peninsula adjacent to Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oilPeople and Society ::OmanNationality:noun: Omani(s)adjective: OmaniEthnic groups:Arab, Baluchi, South Asian (Indian, Pakistani, Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi), AfricanLanguages:Arabic (official), English, Baluchi, Urdu, Indian dialectsReligions:Ibadhi Muslim (official) 75%, other (includes Sunni Muslim, Shia Muslim, Hindu) 25%Population:3,154,134 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 136note: includes 577,293 non-nationalsAge structure:0-14 years: 30.6% (male 494,444/female 469,752)15-24 years: 20.2% (male 333,583/female 302,618)25-54 years: 42.1% (male 781,396/female 547,872)55-64 years: 3.9% (male 65,722/female 56,673)65 years and over: 3.2% (male 51,515/female 50,559) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 35.7 %youth dependency ratio: 31.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 3.8 %potential support ratio: 26.2 (2013)Median age:total: 24.7 yearsmale: 25.9 yearsfemale: 23.1 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:2.06% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Birth rate:24.43 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Death rate:3.4 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 217Net migration rate:-0.47 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Urbanization:urban population: 73.4% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 2.23% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MUSCAT (capital) 634,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.1 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.45 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.17 male(s)/female65 years and over: 1.03 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.22 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Maternal mortality rate:32 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 123Infant mortality rate:total: 14.46 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 115male: 14.76 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 14.15 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 74.72 yearscountry comparison to the world: 105male: 72.84 yearsfemale: 76.7 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.86 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Contraceptive prevalence rate:31.7% (2000)Health expenditures:2.8% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 181Physicians density:1.9 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:1.8 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 93% of populationrural: 78% of populationtotal: 89% of populationunimproved:urban: 7% of populationrural: 22% of populationtotal: 11% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 95% of populationtotal: 99% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 5% of populationtotal: 1% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 153HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1,100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 138HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 116Obesity - adult prevalence rate:20.9% (2008)country comparison to the world: 94Children under the age of 5 years underweight:8.6% (2009)country comparison to the world: 72Education expenditures:4.3% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 102Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 86.9%male: 90.2%female: 81.8% (2010 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 14 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 14 years (2011)Government ::OmanCountry name:conventional long form: Sultanate of Omanconventional short form: Omanlocal long form: Saltanat Umanlocal short form: Umanformer: Muscat and OmanGovernment type:monarchyCapital:name: Muscatgeographic coordinates: 23 37 N, 58 35 Etime difference: UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:11 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazat); Ad Dakhiliyah, Al Buraymi, Al Wusta, Az Zahirah, Janub al Batinah (Al Batinah South), Janub ash Sharqiyah (Ash Sharqiyah South), Masqat (Muscat), Musandam, Shamal al Batinah (Al Batinah North), Shamal ash Sharqiyah (Ash Sharqiyah North), Zufar (Dhofar)Independence:1650 (expulsion of the Portuguese)National holiday:Birthday of Sultan QABOOS, 18 November (1940)Constitution:none; note - on 6 November 1996, Sultan QABOOS issued a royal decree promulgating a basic law considered by the government to be a constitution which, among other things, clarifies the royal succession, provides for a prime minister, bars ministers from holding interests in companies doing business with the government, establishes a bicameral legislature, and guarantees basic civil liberties for Omani citizensLegal system:mixed legal system of Anglo-Saxon law and Islamic lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:21 years of age; universal; note - members of the military and security forces by law are not allowed to voteExecutive branch:chief of state: Sultan and Prime Minister QABOOS bin Said Al-Said (sultan since 23 July 1970 and prime minister since 23 July 1972); note - the monarch is both the chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: Sultan and Prime Minister QABOOS bin Said Al-Said (sultan since 23 July 1970 and prime minister since 23 July 1972)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the monarch(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: the Ruling Family Council determines a successor from the Sultan's extended family; if the Council cannot form a consensus within three days of the Sultan's death or incapacitation, the Defense Council will relay a predetermined heir as chosen by the SultanLegislative branch:bicameral - consists of Majlis al-Dawla or upper chamber (71 seats; members appointed by the sultan; has only advisory powers) and Majlis al-Shura or lower chamber (84 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms; body has authority to draft legislation but is subordinate to the Sultan)elections: (Majlis al-Shura) last held on 15 October 2011 (next to be held in October 2015)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; note - three prominent figures from the Arab Spring 2011 protests won seats; one woman also won a seatJudicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 5 judges)judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the 9-member Supreme Judicial Council (chaired by the monarch) and appointed by the monarch; judge tenure NAsubordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance; sharia courts; magistrates' courtsPolitical parties and leaders:political parties are illegalPolitical pressure groups and leaders:noneInternational organization participation:ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Hunaina bint Sultan bin Ahmad al-MUGHAIRIchancery: 2535 Belmont Road, NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 387-1980FAX: [1] (202) 745-4933Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Greta C. HOLTZembassy: Jamait Ad Duwal Al Arabiyya Street, Al Khuwair area, Muscatmailing address: P. O. Box 202, P.C. 115, Madinat Al Sultan Qaboos, Muscattelephone: [968] 24-643-400FAX: [968] 24-64-37-40Flag description:three horizontal bands of white, red, and green of equal width with a broad, vertical, red band on the hoist side; the national emblem (a khanjar dagger in its sheath superimposed on two crossed swords in scabbards) in white is centered near the top of the vertical band; white represents peace and prosperity, red recalls battles against foreign invaders, and green symbolizes the Jebel Akhdar (Green Mountains) and fertilityNational symbol(s):Khanjar dagger superimposed on two crossed swordsNational anthem:name: ""Nashid as-Salaam as-Sultani"" (The Sultan's Anthem)lyrics/music: Rashid bin Uzayyiz al KHUSAIDI/James Frederick MILLS, arranged by Bernard EBBINGHAUSnote: adopted 1932; new words were written after QABOOS bin Said al Said gained power in 1970; the anthem was first performed by the band of a British ship as a salute to the Sultan during a 1932 visit to Muscat; the bandmaster of the HMS Hawkins was asked to write a salutation to the Sultan on the occasion of his visiting the shipEconomy ::OmanEconomy - overview:Oman is a middle-income economy that is heavily dependent on dwindling oil resources. Because of declining reserves and a rapidly growing labor force, Muscat has actively pursued a development plan that focuses on diversification, industrialization, and privatization, with the objective of reducing the oil sector's contribution to GDP to 9% by 2020 and creating more jobs to employ the rising numbers of Omanis entering the workforce. Tourism and gas-based industries are key components of the government's diversification strategy. However, increases in social welfare benefits, particularly since the Arab Spring, will challenge the government's ability to effectively balance its budget if oil revenues decline. By using enhanced oil recovery techniques, Oman succeeded in increasing oil production, giving the country more time to diversify, and the increase in global oil prices through 2011 provided the government greater financial resources to invest in non-oil sectors. In 2012, continued surpluses resulting from sustained high oil prices and increased enhanced oil recovery allowed the government to maintain growth in social subsidies and public sector job creation. However, the Sultan made widely reported statements indicating this would not be sustainable, and called for expanded efforts to support SME development and entrepreneurship. Government agencies and large oligarchic group companies heeded his call, announcing new initiatives to spin off non-essential functions to entrepreneurs, incubate new businesses, train and mentor up and coming business people, and provide financing for start-ups. In response to fast growth in household indebtedness, the Central Bank reduced the ceiling on personal interest loans from 8 to 7%, lowered mortgage rates, capped the percentage of consumer loans at 50% of borrower's salaries for personal loans and 60% for housing loans, and limited maximum repayment terms to 10 and 25 years respectively. In 2012 the Central Bank also issued final regulations governing Islamic banking and two full-fledged Islamic banks held oversubscribed IPOs while four traditional banks opened sharia-compliant Islamic windows.GDP (purchasing power parity):$91.54 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 76$87.16 billion (2011 est.)$83.41 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$76.46 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 654.5% (2011 est.)5.6% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$29,600 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 51$29,100 (2011 est.)$33,100 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:38% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1241% of GDP (2011 est.)37.9% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 30%government consumption: 17.2%investment in fixed capital: 26.2%exports of goods and services: 61.6%imports of goods and services: -35%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 1%industry: 66%services: 33% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:dates, limes, bananas, alfalfa, vegetables; camels, cattle; fishIndustries:crude oil production and refining, natural and liquefied natural gas (LNG) production; construction, cement, copper, steel, chemicals, optic fiberIndustrial production growth rate:0.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Labor force:968,800country comparison to the world: 143note: about 60% of the labor force is non-national (2007)Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: NA%industry: NA%services: NA%Unemployment rate:15% (2004 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Population below poverty line:NA%Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NA%highest 10%: NA%Budget:revenues: $36.36 billionexpenditures: $27.98 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:47.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):11% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Public debt:4.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1534.6% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.9% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 884.1% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:2% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1430.05% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:5.65% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1386.19% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$9.083 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 78$7.971 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$71.42 billion (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 62$63.16 billion (31 December 2009 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$27.62 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 73$23.18 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$19.72 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 64$20.27 billion (31 December 2010)$17.3 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:$10.22 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 25$10.67 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$52.04 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 59$47.09 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:petroleum, reexports, fish, metals, textilesExports - partners:China 31.9%, Japan 12.9%, UAE 10.1%, South Korea 10%, Thailand 4.4%, Singapore 4.4% (2012)Imports:$26.49 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68$21.5 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, livestock, lubricantsImports - partners:UAE 23.6%, Japan 12.6%, India 8.5%, China 6.4%, US 6.1% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$14.75 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 66$14.37 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$10.18 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 101$9.297 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$NAExchange rates:Omani rials (OMR) per US dollar -0.3845 (2012 est.)0.3845 (2011 est.)0.3845 (2010 est.)0.3845 (2009)0.3845 (2008)Energy ::OmanElectricity - production:18.59 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Electricity - consumption:15.34 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 109Electricity - installed generating capacity:4.202 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Electricity - from fossil fuels:100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Crude oil - production:915,600 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Crude oil - exports:253,100 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Crude oil - proved reserves:4.902 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Refined petroleum products - production:106,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Refined petroleum products - consumption:98,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Refined petroleum products - exports:19,680 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Refined petroleum products - imports:33,150 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Natural gas - production:35.94 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Natural gas - consumption:17.53 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Natural gas - exports:11.49 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Natural gas - imports:1.9 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Natural gas - proved reserves:849.5 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:55.2 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Communications ::OmanTelephones - main lines in use:305,000 (2012)country comparison to the world: 115Telephones - mobile cellular:5.278 million (2012)country comparison to the world: 102Telephone system:general assessment: modern system consisting of open-wire, microwave, and radiotelephone communication stations; limited coaxial cable; domestic satellite system with 8 earth stationsdomestic: fixed-line and mobile-cellular subscribership both increasing with fixed-line phone service gradually being introduced to remote villages using wireless local loop systemsinternational: country code - 968; the Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) and the SEA-ME-WE-3 submarine cable provide connectivity to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat (2008)Broadcast media:1 state-run TV broadcaster; TV stations transmitting from Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen available via satellite TV; state-run radio operates multiple stations; first private radio station began operating in 2007 and 2 additional stations now operating (2007)Internet country code:.omInternet hosts:14,531 (2012)country comparison to the world: 127Internet users:1.465 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 83Transportation ::OmanAirports:132 (2013)country comparison to the world: 44Airports - with paved runways:total: 13over 3,047 m: 72,438 to 3,047 m: 5914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 119over 3,047 m: 22,438 to 3,047 m: 71,524 to 2,437 m: 51914 to 1,523 m: 33under 914 m:26 (2013)Heliports:3 (2013)Pipelines:condensate 106 km; gas 4,224 km; oil 3,558 km; oil/gas/water 33 km; refined products 264 km (2013)Roadways:total: 45,985 kmcountry comparison to the world: 81paved: 29,685 km (includes 1,384 km of expressways)unpaved: 16,300 km (2011)Merchant marine:total: 5country comparison to the world: 125by type: chemical tanker 1, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 3registered in other countries: 15 (Malta 5, Panama 10) (2010)Ports and terminals:Mina' Qabus, Salalah, SuharMilitary ::OmanMilitary branches:Sultan's Armed Forces (SAF): Royal Army of Oman, Royal Navy of Oman, Royal Air Force of Oman (al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Sultanat Oman) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 985,957females age 16-49: 737,812 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 837,886females age 16-49: 642,427 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 31,959female: 30,264 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:11.4% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Transnational Issues ::OmanDisputes - international:boundary agreement reportedly signed and ratified with UAE in 2003 for entire border, including Oman's Musandam Peninsula and Al Madhah exclave, but details of the alignment have not been made public"
Introduction ::OmanBackground:The inhabitants of the area of Oman have long prospered on Indian Ocean trade. In the late 18th century, a newly established sultanate in Muscat signed the first in a series of friendship treaties with Britain. Over time, Oman's dependence on British political and military advisors increased, but it never became a British colony. In 1970, QABOOS bin Said Al-Said overthrew his father, and he has since ruled as sultan. His extensive modernization program has opened the country to the outside world while preserving the longstanding close ties with the UK. Oman's moderate, independent foreign policy has sought to maintain good relations with all Middle Eastern countries. Inspired by the popular uprisings that swept the Middle East and North Africa beginning in January 2011, Omanis began staging marches and demonstrations to demand economic benefits, an end to corruption, and greater political rights. In response to protester demands, QABOOS in 2011 pledged to implement economic and political reforms, such as granting legislative and regulatory powers to the Majlis al-Shura and introducing unemployment benefits. In August 2012, the Sultan announced a royal directive mandating the speedy implementation of a national job creation plan for thousands of public and private sector jobs. As part of the government's efforts to decentralize authority and allow greater citizen participation in local governance, Oman successfully conducted its first municipal council elections in December 2012. Announced by the Sultan in 2011, the municipal councils will have the power to advise the Royal Court on the needs of local districts across Oman's 11 governorates.Geography ::OmanLocation:Middle East, bordering the Arabian Sea, Gulf of Oman, and Persian Gulf, between Yemen and UAEGeographic coordinates:21 00 N, 57 00 EArea:total: 309,500 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 71land: 309,500 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly smaller than KansasLand boundaries:total: 1,374 kmborder countries: Saudi Arabia 676 km, UAE 410 km, Yemen 288 kmCoastline:2,092 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmClimate:dry desert; hot, humid along coast; hot, dry interior; strong southwest summer monsoon (May to September) in far southTerrain:central desert plain, rugged mountains in north and southElevation extremes:lowest point: Arabian Sea 0 mhighest point: Jabal Shams 2,980 mNatural resources:petroleum, copper, asbestos, some marble, limestone, chromium, gypsum, natural gasLand use:arable land: 0.1%permanent crops: 0.12%other: 99.77% (2011)Irrigated land:588.5 sq km (2004)Total renewable water resources:1.4 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 1.32 cu km/yr (10%/1%/88%)per capita: 515.8 cu m/yr (2003)Natural hazards:summer winds often raise large sandstorms and dust storms in interior; periodic droughtsEnvironment - current issues:rising soil salinity; beach pollution from oil spills; limited natural freshwater resourcesEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Whalingsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsGeography - note:strategic location on Musandam Peninsula adjacent to Strait of Hormuz, a vital transit point for world crude oilPeople and Society ::OmanNationality:noun: Omani(s)adjective: OmaniEthnic groups:Arab, Baluchi, South Asian (Indian, Pakistani, Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi), AfricanLanguages:Arabic (official), English, Baluchi, Urdu, Indian dialectsReligions:Ibadhi Muslim (official) 75%, other (includes Sunni Muslim, Shia Muslim, Hindu) 25%Population:3,154,134 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 136note: includes 577,293 non-nationalsAge structure:0-14 years: 30.6% (male 494,444/female 469,752)15-24 years: 20.2% (male 333,583/female 302,618)25-54 years: 42.1% (male 781,396/female 547,872)55-64 years: 3.9% (male 65,722/female 56,673)65 years and over: 3.2% (male 51,515/female 50,559) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 35.7 %youth dependency ratio: 31.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 3.8 %potential support ratio: 26.2 (2013)Median age:total: 24.7 yearsmale: 25.9 yearsfemale: 23.1 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:2.06% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Birth rate:24.43 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 62Death rate:3.4 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 217Net migration rate:-0.47 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 133Urbanization:urban population: 73.4% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 2.23% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:MUSCAT (capital) 634,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.1 male(s)/female25-54 years: 1.45 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.17 male(s)/female65 years and over: 1.03 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.22 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Maternal mortality rate:32 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 123Infant mortality rate:total: 14.46 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 115male: 14.76 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 14.15 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 74.72 yearscountry comparison to the world: 105male: 72.84 yearsfemale: 76.7 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.86 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Contraceptive prevalence rate:31.7% (2000)Health expenditures:2.8% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 181Physicians density:1.9 physicians/1,000 population (2008)Hospital bed density:1.8 beds/1,000 population (2009)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 93% of populationrural: 78% of populationtotal: 89% of populationunimproved:urban: 7% of populationrural: 22% of populationtotal: 11% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 100% of populationrural: 95% of populationtotal: 99% of populationunimproved:urban: 0% of populationrural: 5% of populationtotal: 1% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 153HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:1,100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 138HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 100 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 116Obesity - adult prevalence rate:20.9% (2008)country comparison to the world: 94Children under the age of 5 years underweight:8.6% (2009)country comparison to the world: 72Education expenditures:4.3% of GDP (2009)country comparison to the world: 102Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 86.9%male: 90.2%female: 81.8% (2010 est.)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 14 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 14 years (2011)Government ::OmanCountry name:conventional long form: Sultanate of Omanconventional short form: Omanlocal long form: Saltanat Umanlocal short form: Umanformer: Muscat and OmanGovernment type:monarchyCapital:name: Muscatgeographic coordinates: 23 37 N, 58 35 Etime difference: UTC+4 (9 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)Administrative divisions:11 governorates (muhafazat, singular - muhafazat); Ad Dakhiliyah, Al Buraymi, Al Wusta, Az Zahirah, Janub al Batinah (Al Batinah South), Janub ash Sharqiyah (Ash Sharqiyah South), Masqat (Muscat), Musandam, Shamal al Batinah (Al Batinah North), Shamal ash Sharqiyah (Ash Sharqiyah North), Zufar (Dhofar)Independence:1650 (expulsion of the Portuguese)National holiday:Birthday of Sultan QABOOS, 18 November (1940)Constitution:none; note - on 6 November 1996, Sultan QABOOS issued a royal decree promulgating a basic law considered by the government to be a constitution which, among other things, clarifies the royal succession, provides for a prime minister, bars ministers from holding interests in companies doing business with the government, establishes a bicameral legislature, and guarantees basic civil liberties for Omani citizensLegal system:mixed legal system of Anglo-Saxon law and Islamic lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:21 years of age; universal; note - members of the military and security forces by law are not allowed to voteExecutive branch:chief of state: Sultan and Prime Minister QABOOS bin Said Al-Said (sultan since 23 July 1970 and prime minister since 23 July 1972); note - the monarch is both the chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: Sultan and Prime Minister QABOOS bin Said Al-Said (sultan since 23 July 1970 and prime minister since 23 July 1972)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the monarch(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: the Ruling Family Council determines a successor from the Sultan's extended family; if the Council cannot form a consensus within three days of the Sultan's death or incapacitation, the Defense Council will relay a predetermined heir as chosen by the SultanLegislative branch:bicameral - consists of Majlis al-Dawla or upper chamber (71 seats; members appointed by the sultan; has only advisory powers) and Majlis al-Shura or lower chamber (84 seats; members elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms; body has authority to draft legislation but is subordinate to the Sultan)elections: (Majlis al-Shura) last held on 15 October 2011 (next to be held in October 2015)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NA; note - three prominent figures from the Arab Spring 2011 protests won seats; one woman also won a seatJudicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 5 judges)judge selection and term of office: judges nominated by the 9-member Supreme Judicial Council (chaired by the monarch) and appointed by the monarch; judge tenure NAsubordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Courts of First Instance; sharia courts; magistrates' courtsPolitical parties and leaders:political parties are illegalPolitical pressure groups and leaders:noneInternational organization participation:ABEDA, AFESD, AMF, CAEU, FAO, G-77, GCC, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, LAS, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Hunaina bint Sultan bin Ahmad al-MUGHAIRIchancery: 2535 Belmont Road, NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 387-1980FAX: [1] (202) 745-4933Diplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Greta C. HOLTZembassy: Jamait Ad Duwal Al Arabiyya Street, Al Khuwair area, Muscatmailing address: P. O. Box 202, P.C. 115, Madinat Al Sultan Qaboos, Muscattelephone: [968] 24-643-400FAX: [968] 24-64-37-40Flag description:three horizontal bands of white, red, and green of equal width with a broad, vertical, red band on the hoist side; the national emblem (a khanjar dagger in its sheath superimposed on two crossed swords in scabbards) in white is centered near the top of the vertical band; white represents peace and prosperity, red recalls battles against foreign invaders, and green symbolizes the Jebel Akhdar (Green Mountains) and fertilityNational symbol(s):Khanjar dagger superimposed on two crossed swordsNational anthem:name: ""Nashid as-Salaam as-Sultani"" (The Sultan's Anthem)lyrics/music: Rashid bin Uzayyiz al KHUSAIDI/James Frederick MILLS, arranged by Bernard EBBINGHAUSnote: adopted 1932; new words were written after QABOOS bin Said al Said gained power in 1970; the anthem was first performed by the band of a British ship as a salute to the Sultan during a 1932 visit to Muscat; the bandmaster of the HMS Hawkins was asked to write a salutation to the Sultan on the occasion of his visiting the shipEconomy ::OmanEconomy - overview:Oman is a middle-income economy that is heavily dependent on dwindling oil resources. Because of declining reserves and a rapidly growing labor force, Muscat has actively pursued a development plan that focuses on diversification, industrialization, and privatization, with the objective of reducing the oil sector's contribution to GDP to 9% by 2020 and creating more jobs to employ the rising numbers of Omanis entering the workforce. Tourism and gas-based industries are key components of the government's diversification strategy. However, increases in social welfare benefits, particularly since the Arab Spring, will challenge the government's ability to effectively balance its budget if oil revenues decline. By using enhanced oil recovery techniques, Oman succeeded in increasing oil production, giving the country more time to diversify, and the increase in global oil prices through 2011 provided the government greater financial resources to invest in non-oil sectors. In 2012, continued surpluses resulting from sustained high oil prices and increased enhanced oil recovery allowed the government to maintain growth in social subsidies and public sector job creation. However, the Sultan made widely reported statements indicating this would not be sustainable, and called for expanded efforts to support SME development and entrepreneurship. Government agencies and large oligarchic group companies heeded his call, announcing new initiatives to spin off non-essential functions to entrepreneurs, incubate new businesses, train and mentor up and coming business people, and provide financing for start-ups. In response to fast growth in household indebtedness, the Central Bank reduced the ceiling on personal interest loans from 8 to 7%, lowered mortgage rates, capped the percentage of consumer loans at 50% of borrower's salaries for personal loans and 60% for housing loans, and limited maximum repayment terms to 10 and 25 years respectively. In 2012 the Central Bank also issued final regulations governing Islamic banking and two full-fledged Islamic banks held oversubscribed IPOs while four traditional banks opened sharia-compliant Islamic windows.GDP (purchasing power parity):$91.54 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 76$87.16 billion (2011 est.)$83.41 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$76.46 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 654.5% (2011 est.)5.6% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$29,600 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 51$29,100 (2011 est.)$33,100 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:38% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1241% of GDP (2011 est.)37.9% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 30%government consumption: 17.2%investment in fixed capital: 26.2%exports of goods and services: 61.6%imports of goods and services: -35%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 1%industry: 66%services: 33% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:dates, limes, bananas, alfalfa, vegetables; camels, cattle; fishIndustries:crude oil production and refining, natural and liquefied natural gas (LNG) production; construction, cement, copper, steel, chemicals, optic fiberIndustrial production growth rate:0.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 130Labor force:968,800country comparison to the world: 143note: about 60% of the labor force is non-national (2007)Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: NA%industry: NA%services: NA%Unemployment rate:15% (2004 est.)country comparison to the world: 145Population below poverty line:NA%Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: NA%highest 10%: NA%Budget:revenues: $36.36 billionexpenditures: $27.98 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:47.6% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 18Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):11% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 8Public debt:4.1% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1534.6% of GDP (2011 est.)Fiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):2.9% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 884.1% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:2% (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1430.05% (31 December 2009 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:5.65% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1386.19% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$9.083 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 78$7.971 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$71.42 billion (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 62$63.16 billion (31 December 2009 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$27.62 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 73$23.18 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$19.72 billion (31 December 2011)country comparison to the world: 64$20.27 billion (31 December 2010)$17.3 billion (31 December 2009)Current account balance:$10.22 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 25$10.67 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$52.04 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 59$47.09 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:petroleum, reexports, fish, metals, textilesExports - partners:China 31.9%, Japan 12.9%, UAE 10.1%, South Korea 10%, Thailand 4.4%, Singapore 4.4% (2012)Imports:$26.49 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68$21.5 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:machinery and transport equipment, manufactured goods, food, livestock, lubricantsImports - partners:UAE 23.6%, Japan 12.6%, India 8.5%, China 6.4%, US 6.1% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$14.75 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 66$14.37 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$10.18 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 101$9.297 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$NAExchange rates:Omani rials (OMR) per US dollar -0.3845 (2012 est.)0.3845 (2011 est.)0.3845 (2010 est.)0.3845 (2009)0.3845 (2008)Energy ::OmanElectricity - production:18.59 billion kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Electricity - consumption:15.34 billion kWh (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 76Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 105Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 109Electricity - installed generating capacity:4.202 million kW (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 77Electricity - from fossil fuels:100% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 142Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 184Electricity - from other renewable sources:0% of total installed capacity (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 160Crude oil - production:915,600 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 22Crude oil - exports:253,100 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Crude oil - imports:0 bbl/day (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 99Crude oil - proved reserves:4.902 billion bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 25Refined petroleum products - production:106,000 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 71Refined petroleum products - consumption:98,000 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 79Refined petroleum products - exports:19,680 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 72Refined petroleum products - imports:33,150 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Natural gas - production:35.94 billion cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 26Natural gas - consumption:17.53 billion cu m (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 37Natural gas - exports:11.49 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 20Natural gas - imports:1.9 billion cu m (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 50Natural gas - proved reserves:849.5 billion cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 27Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:55.2 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Communications ::OmanTelephones - main lines in use:305,000 (2012)country comparison to the world: 115Telephones - mobile cellular:5.278 million (2012)country comparison to the world: 102Telephone system:general assessment: modern system consisting of open-wire, microwave, and radiotelephone communication stations; limited coaxial cable; domestic satellite system with 8 earth stationsdomestic: fixed-line and mobile-cellular subscribership both increasing with fixed-line phone service gradually being introduced to remote villages using wireless local loop systemsinternational: country code - 968; the Fiber-Optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) and the SEA-ME-WE-3 submarine cable provide connectivity to Asia, the Middle East, and Europe; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean), 1 Arabsat (2008)Broadcast media:1 state-run TV broadcaster; TV stations transmitting from Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Yemen available via satellite TV; state-run radio operates multiple stations; first private radio station began operating in 2007 and 2 additional stations now operating (2007)Internet country code:.omInternet hosts:14,531 (2012)country comparison to the world: 127Internet users:1.465 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 83Transportation ::OmanAirports:132 (2013)country comparison to the world: 44Airports - with paved runways:total: 13over 3,047 m: 72,438 to 3,047 m: 5914 to 1,523 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 119over 3,047 m: 22,438 to 3,047 m: 71,524 to 2,437 m: 51914 to 1,523 m: 33under 914 m:26 (2013)Heliports:3 (2013)Pipelines:condensate 106 km; gas 4,224 km; oil 3,558 km; oil/gas/water 33 km; refined products 264 km (2013)Roadways:total: 45,985 kmcountry comparison to the world: 81paved: 29,685 km (includes 1,384 km of expressways)unpaved: 16,300 km (2011)Merchant marine:total: 5country comparison to the world: 125by type: chemical tanker 1, passenger 1, passenger/cargo 3registered in other countries: 15 (Malta 5, Panama 10) (2010)Ports and terminals:Mina' Qabus, Salalah, SuharMilitary ::OmanMilitary branches:Sultan's Armed Forces (SAF): Royal Army of Oman, Royal Navy of Oman, Royal Air Force of Oman (al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Sultanat Oman) (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-30 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 985,957females age 16-49: 737,812 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 837,886females age 16-49: 642,427 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 31,959female: 30,264 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:11.4% of GDP (2005 est.)country comparison to the world: 1Transnational Issues ::OmanDisputes - international:boundary agreement reportedly signed and ratified with UAE in 2003 for entire border, including Oman's Musandam Peninsula and Al Madhah exclave, but details of the alignment have not been made public"
The World Factbook. 2014.
